Abstract
Introduction: The incidence of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) is increasing, especially in people over 60 years of age. This population usually has a worse prognosis, probably due to comorbidities, functional deterioration and decreased tolerance to treatment. Therefore, a pre-therapeutic evaluation would be important to make decisions. The Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA) is the recommended tool for this evaluation, but it is a complex process that demands time and resources. We performed a study to evaluate the characteristics of the CGA in patients >64 years of age with NHL and to determine which domains can constitute a simplified model.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study with retrospective data collection of geriatric evaluations performed in >64 years with aggressive NHL (90% DLBCL, 10% PTCL) admitted to our institution between September 2015 and August 2017. Number of drugs, prescriptions in older adults was evaluated (STOPP), Lawton scale, Barthel scale, KATZ index, walking speed, Up and Go time (TUG), Mini-mental test, Yesavage scale, Gijón scale, Mini-nutritional, Geriatric syndromes (Incontinence, Falls, Pressure ulcers, Immobility, Sensory Deficits, Osteoporosis), and Accumulated Disease Scale in Geriatrics (CIRS-G). The CGA included 9 domains, and fragility was defined as deterioration in >2 domains. The different evaluations were compared with fragility. Multivariate models were constructed using logistic regression.
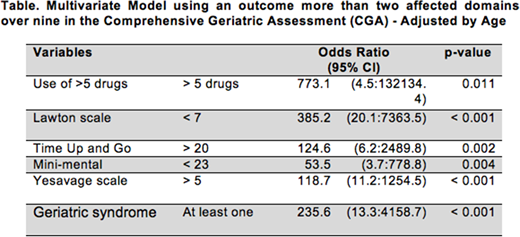
Results: We included 253 patients with an average age of 76 years. 62% had >1 affected domain, and 40% were considered fragile (>2 affected domains). In the bivariate analysis, age >85 years, and all the geriatric scales except STOPP, were strongly associated with fragility. The final model had 6 variables: Use of >5 drugs ( OR 773.1, 95% CI,4.5-132134.4;p=0.011), Lawton scale <7 (OR 385.2,95%CI, 20.1-7363.5;p<0.001), TUG >20 (OR 124.6,95%CI, 6.2-2489.8;p=0.002), Mini-mental <23 (OR 53.5,95%CI, 3.7-778.8;p=0.004),Yesavage scale >5 (OR 118.7,95%CI, 11.2-1254.5;p<0.001), and presence of at least one geriatric syndrome (OR 235.6,95%CI, 13.3-4158.7;p<0.001). Removing the Mini-mental minimally affected the model, but suppressing two or more variables does weaken the model.
Conclusions: In our cohort of patients older than 64 years with aggressive NHL, a model based on five measurements (i.e. number of drugs, TUG, Lawton scale, Yesavage scale and Geriatric Syndromes) could constitute an evaluation with an efficiency similar to a complete CGA.
Castillo:Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy; Millennium: Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Beigene: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal